Topic We Cover: CA vs CS
1. Chartered Accountant (CA)
2. Chartered Accountancy in India
3. CA Common Proficiency Test (CPT)
- Exam Pattern of CPT
- Accounting
- Mercantile Law
- General Economics
- Quantitative Aptitude
4. Integrated Professional Competence Course (IPCC)
5. CA Finals
6. Company Secretary
- Foundation Programme
- Executive Programme
- CS Professional Course
7. Cost and Management Accountant (CMA)
- Foundation Course
- CMA Intermediate Course
- CMA Final Examination
8. Chartered Financial Analyst
9. CA v CS v CMA v CFA

Professional commerce course are in high demand across the country due to demand for specific skill set
CA vs CS, these names ring alarm bells for commerce students across in India. Thousands upon thousands of students in India dream of achieving the elusive dream of becoming a CA or CS. In a country where opportunities to succeed are limited to some extent, becoming a part of an elite group of professionals is nothing short of monumental. The drive to become CA and CS is borne of the ambition of reaching the top of the food chain. The question which arises though, which is better? CA or CS?
In general, both fields are extremely technical and require an incredible amount of numerical ability and mathematical discipline. Thus, if mathematics isn’t your cup of tea, it is better to steer clear of CA and CS. Only an incredible amount of perseverance with numbers and statistics will make you clear your CA Exams, let alone become a good CA. Similarly, CS also involves a decent amount of mathematics and statistics. Although the focus in CS is more on the legal side of things, the job itself involves a plenty amount of number crunching.
Before making an assertion over which of the two is better, delving deeper is necessary. Many students are baptized with fire as they commence their CA and CS Preparation. The most important thing to do before starting your CA or CS preparation is to dismiss the notion of not doing graduation. Self-belief is one thing and self-aggrandizing is another?
Pursuing CA exams without having the backup of a graduate degree is almost like skydiving without a parachute. CA may seem an incredible profession, but reaching the top of the mountain requires crossing some very treacherous roads. In the worst case scenario, it is always better to have a graduate degree. Besides opening up job scenarios, you can even pursue MBA entrance exams in India and abroad.
Chartered Accountant (CA)
Indians are often found guilty of knowing every concept superficially. Someone may advise you to take up CA preparation, but when pressed on the scope of the field or the saturation level of the industry, they will often shrug it off. This cavalier approach is not only callous but dangerous too.
Chartered Accountancy is essentially a postgraduate title given to an accountant after completion of a given set of courses. All activities which include formulating of financial strategies, planning long-term investments and pension funds, mergers and acquisition strategies and diligence of investments fall under the purview of CAs.
Many top business executives at major corporations started off their careers in accounting. The aptitude to gauge numbers and deal with statistics and data on a daily basis is embedded in CAs.
Chartered Accountancy in India
The scope of CA in India is limitless as of this moment. Fields such as engineering are slowly fizzling out due to lack of growth opportunities and students are still keen on pursuing it. CA studies haven’t even reached that amount of craze amongst students.
In India, CA studies and titles are managed by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India. Chartered Accountancy is essentially a distance learning course with exams scheduled annually in the month of May conducted by ICAI. The complete procedure for becoming a CA is given as follows.
1. CA Common Proficiency Test (CPT)
CPT is the first step to becoming a CA. Held twice every year, CPT is compulsory for candidates without a graduate degree in commerce. Candidates can appear for CA –CPT after 10+2. The exam is held in June and December.
The details of CPT are tabulated below:
|
Mode of examination |
Pen and Paper based |
|
Medium |
Hindi/English |
|
Number of sessions |
CPT is held in two sessions. |
|
Time |
10 am – 12pm for Session 1 and 2-4 pm for Session 2 |
|
Duration |
Four hours as each session is two hours long |
|
Question Type |
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |
|
Number of questions |
200 |
|
Maximum Marks |
200 |
|
Negative Marking |
0.25 mark is deducted for every wrong answer |
Online application form is available on the official ICAI website for Rs. 500. Offline forms can be obtained from ICAI Bhawan, Indraprastha Marg, New Delhi for Rs. 1500. With this obvious gap in fee, it is advisable to register online and save money.
Exam Pattern of CPT
|
Session and timings |
Sections |
Questions |
|
First Session (10am to 12pm) |
Fundamentals of Accounting |
40 |
|
Mercantile Law |
60 |
|
|
Second Session (2-4 pm) |
General Economics |
50 |
|
Quantitative Aptitude |
50 |
These sections are very specific and are in the domain of commerce students in general. However, ICAI throws a wide net for students. Candidates from any background can appear for CPT provided they had taken mathematics as a subject during 10+2. Many engineering students appear for CPT too, though they generally have to attend coaching classes to cope with some core commerce classes.
The in depth syllabus of CA CPT is given below.
Accounting
Accounting is considered the toughest subject in commerce by students and teachers alike. To be a CA though, you’ll have to be tough as a nail in this department. Some of the topics are listed below
- Theoretical Framework
- Accounting Processes
- Reconciliation Statement of Banks
- Accounting of depreciation
- Preparation of Final Accounts for Sole Proprietors
- Special Transactions accounting
- Partnership Accounts
- Company Accounts
Mercantile Law
This involves studying laws and acts pertaining to trade passed by governments over the years. Some of the important topics are
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872: Sections 1-75 covering contents of contracts, performance and breach of contract.
- The Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Developing contract of sale, conditions, warranties, transfer of ownership and goods delivery.
- The Indian Partnership Act, 1932: General structure of partnership, rights, and duties of partners, registration and dissolution of a firm.
General Economics
Economics is an essential topic for future CAs to concentrate upon. Knowing the inner workings of how markets work and fluctuate is important for any CA to know. Important topics for CPT are listed below
- Micro Economics
- Theory of Production and Cost
- Price Determination in Different Markets
- Indian Economic Development
- Introduction to Micro Economics
- Money and Banking
- Theory of Demand and Supply
- Indian Economy – A Profile
- Select Aspects of Indian Economy
- Economic Reforms in India
Quantitative Aptitude
Quants are an essential part of any entrance exam, and CA-CPT is no exception. Since most CAs are expected to be top class in mathematics, what better way is there to test a candidate’s math skills than quants? Besides general quant questions, many mainstream math topics are also covered under this section.
- Ratio and proportion, Indices, Logarithms
- Simple and Compound Interest including annuity
- Inequalities
- Basic concepts of Differential and Integral Calculus
- Statistics
- Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion
- Permutations and Combinations
- Sequence and Series
- Sets, Functions and Relations
- Limits and Continuity
- Theoretical Distributions
- Sampling Theory
- Correlation and Regression
- Index Numbers
2. Integrated Professional Competence Course (IPCC)
IPCC is an intermediary course to CA Finals. It comprises two groups of subjects which have to be cleared to move forward. These subjects are a notch above CPT Level and prompt extreme preparation and dedication to clear.
Most students fail to clear IPCC in their first attempt simply due to the tedious nature of the exams. The pass percentage for IPCC May 2017 Group 1 was 16.19% and 21.47% for Group 2.
IPCC Group 1 and 2 consists of the following.
Group 1
- Paper 1: Accounting
- Paper 2: Business Laws, Ethics and Communication
- Paper 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management
- Paper 4: Tax
Group 2
- Paper 5: Advanced Accounting
- Paper 6: Auditing and Assurance
- Paper 7: IT and Strategic Management
After clearing IPCC, CA aspirants have to complete two and a half year articleship at CA firms. Don’t mistake articleship for a mere internship. Unlike the latter, an articleship is far more exhaustive and tedious. Since the firms know that your CA title is at stake, you’ll be made to slog harder and longer for three years.
3. CA Finals
Atop Mount Doom sit CA Finals. The toughest of all previous exams, CA Finals are effectively close to post-graduate level exams testing not only technical but a candidate’s mental toughness as well. Most CAs take 3-5 years to finish CA Finals on an average. While ICAI tries to justify this low pass percentage down to maintaining supply and demand, students often feel mentally slaughtered after seeing so many years of their youth wasted on a ‘alleged’ pipe dream.
CA Finals comprise of eight papers divided into two groups. These papers are
Group 1
- Paper 1: Financial Reporting
- Paper 2: Strategic Financial Management
- Paper 3: Advanced Auditing and Professional Ethics
- Paper 4: Corporate and Allied Laws
Group 2
- Paper 5: Advanced Management Accounting
- Paper 6: Information Systems Control and Audit
- Paper 7: Direct Tax Laws
- Paper 8: Indirect Tax Laws
Clearing these papers is the final hurdle between being someone and being a CA. Many toil for years, but the moment you clear the Finals, you become a CA for life!
Company Secretary
Many often group CS and CA in the same basket of courses, and rightly so. Many topics in CA and CS do overlap over time, but in the jobs market, both digress completely to perform different roles.
A company secretary is essentially an in-house legal advisor demarcating the working of a company based upon certain guidelines and rules set by the government. CS ensures companies work within a set framework and comply with certain guidelines which have to be followed. Every listed company in India has to employ a company secretary in a key managerial position to ensure smooth functioning within certain given rules.
Becoming a CS involves three steps.
1. Foundation Programme
Foundation course is the first step involved to becoming a CS. An eight month course conducted by the Institute of Company Secretaries in India (ICSI) is an in depth study of the fundamentals a typical company secretary has to cover. These topics include legal entities of taxation, labor laws, corporate laws, accounting and financial analysis. CS like CA is a distance learning course although many students do go for coaching classes for preparation.
The Foundation course exam essentially contains four different topics
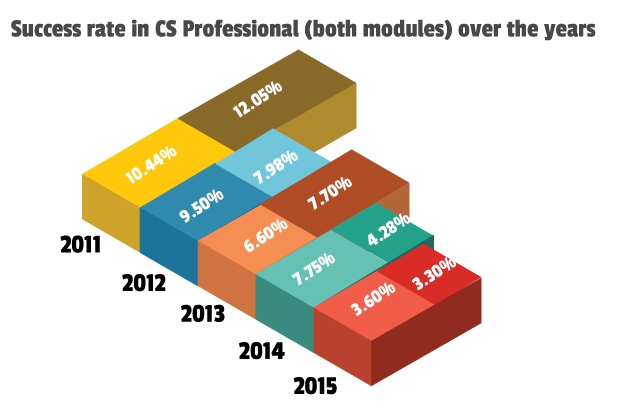
Pass percentage of candidates appearing in CS Professional exams in the months of June and December
- Business Environment and Entrepreneurship
- Business Management Ethics and Communication
- Business Economics
- Fundamentals of Accounting and Auditing
Only candidates who have completed secondary education can appear for the Foundation course. Registrations can be done round the year, but to sit for a particular exam registration has to be done eight months prior.
 Get Updated Review ( Voice Based Alumni Feeback)
Get Updated Review ( Voice Based Alumni Feeback)
-
 Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Lovely Professional University - [LPU] – Click Here
Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Lovely Professional University - [LPU] – Click Here -
 Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Amity University – Click Here
Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Amity University – Click Here -
 Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - UPES Dehradoon – Click Here
Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - UPES Dehradoon – Click Here -
 Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - SRM University Sonipat – Click Here
Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - SRM University Sonipat – Click Here -
 Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Ansal University – Click Here
Check Review (Alumni Feedback) - Ansal University – Click Here
CS Foundation registration fee is Rs 4500 and the examination fee is Rs 1200. If a candidate wishes to appear for the CS foundation exam in December, he/she will have to register for the exam before March 31. Likewise, for June 2018 exam, registration has to be done before 30 September 2017.
The exam will be in a computer-based objective type format. No negative marks shall be awarded for wrong answers
2. Executive Programme
Like CA-IPCC, the executive programme is also essentially an intermediate programme. Divided into two modules containing seven subjects in total, CS executive delves further into the legal framework of the functioning of a company and its activities.
Students can appear for one single module or both modules together, but the deadline for registration differs
- February 28 for both modules in December
- May 31 for single module in December
- August 31 for both modules in June
- October 31 for single module in June
Module 1 contains four exams
- Company Law
- Cost and management accounting
- Economic and commercial laws
- Tax Laws and Practice
Module 2 contains three exams
- Company accounts and Auditing practices
- Capital markets and Securities laws
- Industrial, Labor and General laws
The fee for registration for executive programme differs for different candidates
|
Applicant Qualification |
CS Executive course fee |
|
Commerce Graduates |
Rs. 9000/- |
|
CPT/ Foundation passes from ICAI |
Rs. 12,500/- |
|
Non Commerce students |
Rs. 10,000/- |
|
CS Foundation course cleared |
Rs 8,500/- |
Examination fee for each module is Rs 1200/-
3. CS Professional Course
CS Professional course are the final set of exams needed to be cleared for becoming a CS. Like CA Finals, many students sometimes take multiple attempts to clear all the modules. There are namely three modules containing nine subjects in total.
This CS course can be attempted by only those who have cleared the Executive programme. Course fee for the professional course is Rs. 12,000/- and examination fee for every module is Rs. 1200/-
The subjects are divided into the three modules as follows
|
Module 1 |
Advanced Company Law and Practice |
|
Secretarial Audit, Compliance Management and Due Diligence |
|
|
Corporate Restructuring, Valuation and Insolvency |
|
|
Module 2 |
IT and Systems Audit |
|
Financial, Treasury and Forex Management |
|
|
Ethics, Governance and Sustainability |
|
|
Module 3 |
Advanced Tax Laws and Practices |
|
Drafting, Appearances and Pleadings |
|
|
Electives: One out of the following five · Banking Law and Practice · Capital Commodity and Money Market · Insurance Law and Practice · Intellectual Property Rights- Law and Practice · International Business- Laws and Practice |
All three courses of CS can be given in both English and Hindi except Business Communication in the Foundation course.
Besides clearing these three courses, candidates have to undergo a 15 month long training period under a qualified CS or a CS firm. Training can be done after clearing Executive programme or Professional programme.
The training period for each component has been specified by ICSI.
|
Training Component |
Duration |
|
Computer Training |
70 hours |
|
Student Induction Programme (SIP) |
7 days |
|
Executive Development Programme (EDP) |
8 days |
|
Long term internship |
15 months |
|
Professional Development Programme (PDP) |
25 hours |
|
Training with specialized agency |
15 days |
|
Management Skills Orientation Programme |
15 days |
After completion of all the aforementioned courses and training, a candidate can proudly prefix ‘CS’ to their name.
CA V CS: Are there more or do these two define the field?
The clamor amongst commerce students for CA and CS is understandable. Both prospects promise the best possible scenarios a commerce student can hope for. In the chaos of multiple exams, one often forgets there are other professional courses besides CA and CS. Two examples of these professional courses are CMA and CFA.
Cost and Management Accountant (CMA)
A Cost and Management Accountant is tasked with managing expenditure based on available resources and providing sound financial planning. Though CMA’s purview is less diverse than their CA counterparts, they are essential for the smooth functioning of a company as they keep tab and collate where resources should be allocated.
Like CA and CS courses, CMA involves completion of three courses offered by the Institute of Cost Accountants in India (ICAI).
1. Foundation Course
Students who cleared 10+2 can apply for the eight month long CMA Foundation course conducted by ICAI. The course entails eight different papers with different weightage set for different topics. Comprehensive details are tabulated below.
|
Paper Number |
Subject |
Topics |
Weightage |
|
Paper 1 |
Fundamentals of Economics and Management |
Fundamentals of Economics |
50% |
|
Fundamentals of Management |
50% |
||
|
Paper 2 |
Fundamentals of Accounting |
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting |
60% |
|
Fundamentals of Cost and Management Accounting |
40% |
||
|
Paper 3 |
Fundamentals of Laws and Ethics |
Fundamentals of Commercial and Industrial Laws |
80% |
|
Fundamentals of Ethics |
20% |
||
|
Paper 4 |
Fundamentals of Business Mathematics and Statistics |
Fundamentals of Business Mathematics |
40% |
|
Fundamentals of Business Ethics |
60% |
The Foundation exam is held quarterly every year in an objective type question format. The examination fee is Rs. 1200/-
The CMA Foundation course fee is Rs. 4000/-. To sit in June exam, the fee has to be paid by January 31 and for December exam, the deadline is July 31.
2. CMA Intermediate Course
The intermediate course dives deeper into specificity as core subjects of accountancy are lined up across two groups.
Module 3
- Paper 1: Financial Accounting
- Paper 2: Laws and Ethics
- Paper 3: Direct Taxation
- Paper 4: Cost Accounting
Module 4:
- Paper 5: Operations and Strategic Management
- Paper 6: Cost and Management Accounting and Financial Management
- Paper 7: Indirect Taxation
- Paper 8: Company Accounts and Audits
The intermediate course fee is Rs. 20,000/-. The option to pay in installments is also made available to candidates. Rs. 12,000 can be paid during registration
3. CMA Final Examination
CMA finals are the last exams to be cleared to officially become a Cost and Management
Accountant. The course fee for the finals is Rs. 17,000/- which has to be paid as a lump sum amount.
Module 5
Paper 13 – Corporate Laws & Compliance
Paper 14 – Strategic Financial Management
Module 6
Paper 15 – Strategic Cost Management & Business Strategy
Paper 16 – Advanced Direct Tax Laws and International Taxation
Module 7
Paper 17 – Cost and Management Audit
Paper 18 – Financial Analysis and Reporting
Module 8
Paper 19 – Advanced Indirect Tax – Laws & Practice
Paper 20 – “Optional” to be selected from “Specialization Papers”
Optional papers include Strategic Performance Management and Business Valuation, International Business, Treasury Management, Security Analysis and Portfolio Management, Project Management and Control and Supply Chain Management.
Before giving CMA Finals, a candidate has to undergo at least six months in training. In total, to be awarded CMA degree, three years of training has to be done under a qualified CMA or a firm.
Chartered Financial Analyst
Chartered Financial Analyst is a designation awarded by the CFA Institute, US. Though CFA was also being awarded by ICFAI, a lawsuit caused the Indian CFA institute to phase out its CFA programme. Candidates thinking of pursuing CFA will have to register with the international CFA Institute based in USA.
CFA is a renowned designation known worldwide as one of the financial world’s most coveted positions. Unlike other aforementioned fields like CA and CS, CFA is a very dynamic job which is predicated upon gauging market fluctuations and devising investment plans accordingly. Many MBA aspirants end up becoming CFA due to the technical ineptness of MBA versus CFA.
Becoming a CFA requires clearing three levels of exams, Level I, II and III. Only graduates can apply for CFA Level 1 exam along with professionals with at least four years of professional experience.
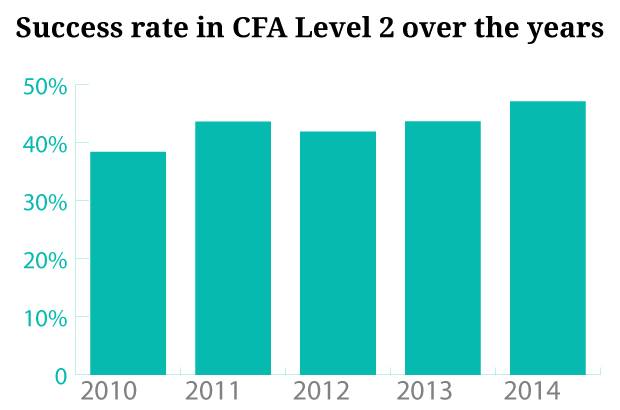
CFA has a much higher success rate compared to other professional course exams in India
1. Level 1 CFA Exam
Level 1 CFA Exams is 240 questions long exam split into two-three hour sessions. The CFA course fee for all three levels is collected during exam registration itself. The course fee is set at $450 and exam fee at $650 (early registration) tallying total amount to $1,100.
Exam sections and their respective weightages are tabulated below.
|
Section |
Weightage |
|
Ethical and Professional Standards |
15% |
|
Quantitative Methods |
12% |
|
Economics |
10% |
|
Financial Reporting and Analysis |
20% |
|
Corporate Finance |
7% |
|
Portfolio Management |
7% |
|
Equity |
10% |
|
Fixed Income |
10% |
|
Derivatives |
5% |
|
Alternative Investments |
4% |
2. CFA Level II Exams
Level II CFA exams consist of typical descriptive questions. A total of twenty vignettes divided equally across two sessions, morning and evening. Each vignette has six questions carrying three marks each, taking the maximum marks tally to 360.
|
Section |
Weightage |
|
Ethics and Professional Standards |
10-15% |
|
Quantitative Methods |
5-10% |
|
Economics |
5-10% |
|
Financial Reporting and Analysis |
15-20% |
|
Corporate Finance |
5-15% |
|
Equity Evaluation |
15-25% |
|
Fixed Income |
10-20% |
|
Derivative Investment |
5-15% |
|
Alternative Investment |
5-10% |
|
Portfolio Management |
5-10% |
3. CFA Level III Exams
The final obstacle in becoming a certified CFA, Level III exams entails 8-12 essay questions containing various subparts in the morning session. The afternoon session is similar to Level II exam with 10 vignettes carrying six questions awarding three marks each.
Level III exam fee is $650 (early registration). Exam sections are listed below.
- Ethical and Professional Standards
- Behavioral Finance, Individual Investors and Institutional Investors
- Capital Market Expectations
- Asset Allocation
- Fixed Income and Equity Management Portfolio
- Alternative Investments, Risk Management and Application of Derivatives
- Portfolio: Execution, Evaluation and Attribution, and Global Investment Performance Standards
CA v CS v CMA v CFA
It was always coming down to this.
Four pillars of the financial world, choosing amongst these four is stepping into a minefield. Each is different and challenging in its own way, offering different packages and challenges along the way.
Is money the defining factor? Money is the language of commerce and forms the very fabric of the financial sector, but is it enough to decide which career is best for you?
Aptitude is a subjective parameter. While it holds paramount importance while choosing best fields of study, there is no quantifiable metric which can be used to incorporate aptitude in a model for comparative analysis.
The factors which will be used to compare the different fields of study in commerce are:
- Average salary
- Average length of course
- Selection percentage
- Demand in India
- Demand abroad
|
Course |
Average Salary (Starting package) |
Average length of course |
Selection percentage (in Finals) |
Demand in India (Out of 5) |
Demand Abroad (Out of 5) |
|
Chartered Accountant (CA) |
Rs. 7.36 LPA |
Official Length: 4 years |
22.98% (May 2017) |
4.5 With the adoption of new financial policies such as GST in India, CAs will continue to be in huge demand for the coming 5-10 years |
3.0 Indian CAs have similar salary, if not less, in countries like Canada and Australia. Besides a difference in lifestyle, there isn’t a greater scope abroad relative to India |
|
Actual length: 7-8 years |
|||||
|
Company Secretary (CS) |
Rs. 4.99 LPA |
Official Length: 4 years |
2.99% (June 2017) |
4.0 Like CAs, companies depend on CSs to guide them through a time where financial reform is first on the government’s agenda |
2.5 Since CS is based on guiding companies from a legal standpoint, Indian CS need to study financial frameworks of specific countries. Thus Indian CS find it difficult to flourish abroad |
|
Actual Length: 5-6 years |
|||||
|
Cost and Management Accountant (CMA) |
Rs. 4.13 LPA |
Official Length: 3.5 years |
12.71% (December 2016) |
3.9 CMA isn’t as popular as CA or CS, but its almost as useful. The financial world is always in need of people with top draw accounting skills |
3.5 CMA is considered a global course due to common accounting practices around the globe. Unlike CS, CMAs find it much easier to find jobs abroad due to similarity in course material |
|
Actual Length: 4-5 years |
|||||
|
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) |
Rs. 3 LPA |
Official Length: 2 years |
54% (June 2017) |
3.6 CFA hasn’t taken off as a profession in India due to the obsession with MBA. However, CFA is a far more technical and diverse subject than MBA, involving market analysis and investment planning. |
4.2 CFA is a course made to pursue opportunities abroad. Developed countries with stable economies need a constant supply of top-grade financial analysts. While starting salaries for CFA in India is low, the situation changes while applying abroad where CFAs are amongst the highest earners. |
|
Actual Length: 3-4 years |
Aptitude and Skills: What does one need to become a finance professional?
Before jumping head-first into the perilous waters of professional courses like CA or CFA, many aspirants tend to ignore the necessary skill set required to ace these courses. The evergreen trend of banking on hard work and iron will is fine, but ignoring the obvious requirements of becoming a successful professional are often ignored.
This is where many students make mistakes every year. Chartered Accountancy or Company Secretary Courses aren’t resume building courses, but career-defining fields of study. To simply pursue these courses out of peer pressure or salary growth is wrong.
CAs, CSs, CMAs and CFAs are experts in their respective field. Each of them is expected to be proficient in handling problems of their field of study. Even if you manage to somehow clear all the exams, there is no point in being a bad CA, as no one will ever hire a semi-professional to handle financial problems. Thus, it is of great importance to have a certain aptitude in mathematics and statistics while thinking of pursuing professional commerce courses.
CA Final Topper 2017 : Mr. Mohit Gupta has emerged as the all India CA Topper by securing AIR 1
CS Final Topper 2017 : Mr. Ranjith Kumara Dasa Ramesh Babu has emerged as the all India CS Topper by securing AIR 1



.jpg)

